Fujitsu, in collaboration with the Japan Institute of Materials and Materials Research, has developed a groundbreaking technology that uses the supercomputer "K" to simulate large-scale magnetization reversal in magnetic materials. Magnetization reversal occurs when the direction of magnetization in a material changes under the influence of an external magnetic field or electric current. This is the first time such a large-scale simulation of permanent magnet reversal has been achieved globally.
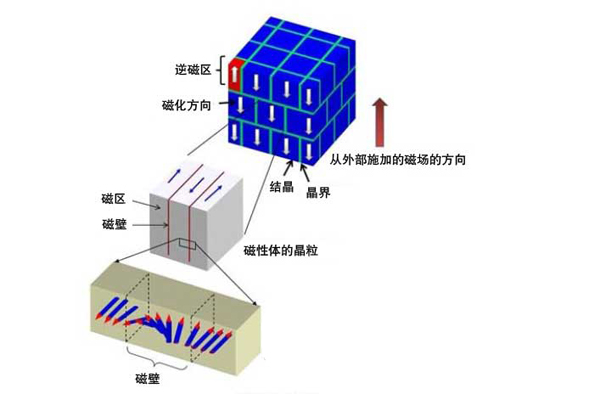
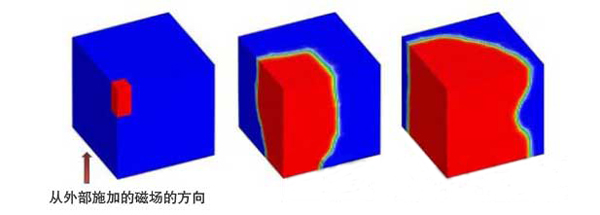
Traditionally, studying magnetization reversal has been extremely challenging due to the immense computational power required, especially for strong neodymium magnets. To overcome this, Fujitsu combined micro-magnetism—a method that analyzes the magnetic state at the atomic level—with the finite element method. This allowed them to create a highly detailed model of a neodymium magnet, divided into regions as small as 1 nanometer. These complex calculations were performed using the supercomputer "K," enabling the successful simulation of magnetization reversal.
This new technology allows researchers to analyze the microscopic magnetic structures that were previously impossible to study with conventional methods. It holds great promise for the development of next-generation magnetic materials, including neodymium magnets that do not rely on heavy rare earth elements like dysprosium. This advancement could significantly impact industries such as electronics, automotive, and renewable energy, where high-performance magnets are essential.
(Reporter: Enohara Hiroyuki, "Nikkei Manufacturing")
Gate Valves,Gate Valve ,Slide Gate Valve,Sluice Gate Valve
WENZHOU DIYE VALVE&FITTINGS CO.,LTD , https://www.diye-valve.com
