Analysis of basic elements of trapezoidal thread
The domestic trapezoidal thread is mainly made of metric thread. The relevant standard number is GB/T5796.1~4-2005, and the tooth angle is 30°. The tooth shape is shown in Figure 1. The calculation formula of the basic elements is shown in Table 2-6.
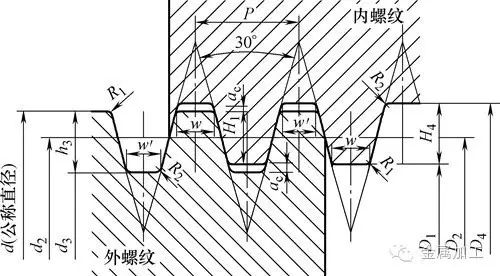
Figure 1 trapezoidal thread profile
Analysis of trapezoidal thread structure and turning characteristics
Trapezoidal threads differ from ordinary threads in that they have a large pitch and a deep cut, making it easy to tie a knife when roughing. At the same time, the cutting force and cutting heat are large, and the tool heat dissipation conditions are poor, which limits the improvement of the cutting speed. If only the conventional programming commands G32 and G92 are used, the tool is fed in the normal radial feed mode. As a result, the three cutting edges are simultaneously cut, which is very difficult to process the trapezoidal thread. Although the G76 command is a lateral feed, mainly for two-edge cutting, but for a trapezoidal thread with an increased pitch, it cuts to a certain depth, and the length of the participating cutting edge is still too large. Therefore, for trapezoidal threads, G76 is generally Only for single thread machining with pitch less than 3 ~ 4mm. For multi-thread threads, especially for trapezoidal threads with a slightly larger pitch, it is generally necessary to program the left and right cutters of the trapezoidal thread on a common lathe, or layered machining, based on the threading instructions provided by the CNC system. Processing in other ways.
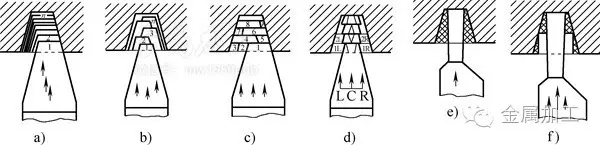
Figure 2 shows the common roughing cutting method for trapezoidal threads.
Figure 2 Trapezoidal thread common rough cutting cutting method
a) Lateral cutting method b) Left and right alternate cutting method c) Layered cutting method d) Left and right layering cutting method e) Straight groove method f) Car step groove methodThe lateral feed cutting method (Fig. 2a) is suitable for direct programming of the G76 command and can be used for roughing and finishing at the same time. It is suitable for machining with a lead (pitch) of less than 4mm thread.
For threading with a lead (pitch) greater than 4 mm, the cutting method shown in Figures 2b to d is generally required. The actual cutting edge except the first one is basically two-edge cutting. Figure 2b shows the left and right alternate cutting method, with each knife alternately cutting into the infeed. Figure 2c shows the layered cutting method, which cuts the radial cut into the depth, and each layer is divided into multiple cuts, which is suitable for threading with large lead. Figure 2d shows the left and right layered cutting method, which also cuts the radial cut into the depth layer, but only the middle, left and right cuts of each layer are completed. These cutting methods generally require the tool left and right movement command (G00 or G01) to complete the programming with the existing thread machining instructions.
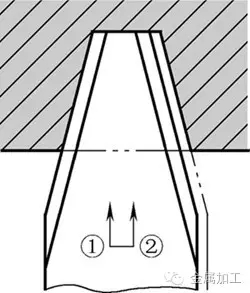
Figure 3 Trapezoidal thread finishing car cutting methodFor threads with a large pitch, you can also use the grooving tool slot (straight or stepped groove) to rough the car, as shown in Figure 2e, f, and then finish the car as shown in Figure 3. This method is suitable for roughing of larger threads with lead (pitch).
Trapezoidal thread layering cutting programming
1. Processing principle
The machining principle of the layered cutting method is shown in Fig. 2c and d. During the machining process, except for the first knives of each layer, which are three-blade cutting, the other knives avoid three-edge cutting. That is to say, the cutting force of the first knives of each layer is the largest, and the cutting depth of each layer is the same. Then, as long as the first knives of the first layer are not knives, the subsequent processing is basically no longer tied. Knife. It can be seen that this method can minimize the three-edge cutting and reduce the cutting area of ​​the tool, thereby reducing the cutting force. When machining, it is only necessary to select the cutting parameters according to the rigidity of the machine tool, workpiece and tool, and the phenomenon of knives can be completely avoided.
2. Problem to be solved
When each layer is cut into the next layer of cutting, the first knife in point must be offset by a distance in the axial direction, and the last knife is also offset by a distance in the axial direction. The offset distances of the two segments are opposite. The offset distance Z is equal to the product of the back-feeding amount ap and the half-angle α /2 tangent function, ie Z = aptan (α /2).
The layered cutting method can not be directly programmed by the system's own thread processing instructions G32, G92 and G76. If it is programmed with ordinary program, since it can only use constant values, it can not be used in calculation and can only be executed sequentially. It is cumbersome, complicated, and error-prone, so macro programming is often used.
Trinexapac-ethyl is a synthetic plant growth regulator that is derived from cyclohexanecarboxylate. Trinexapac-ethyl is used to control the growth on various grass species and crops. Trinexpac-ethyl is applied as a foliar spray, post-emergence, and is translocated to the growing shoot.
Trinexapac-ethyl as an inhibitor of the action of a key enzyme in the formation of GA1, preventing the formation of the Plant Growth Regulator gibberllins, which promotes cell elongation.In the absence of gibberellins the internodes of the plants fail to grow and prevent the plant from growing taller. This can be used to prevent lodging in crops and amenity turf, increase the yield in crops by redirecting energy into the production of reproductive parts and finally to reduce the frequency of mowing in turf.Trinexapac-ethyl is approved for use on cereal crops such as barley, durum wheat, oats, rye, triticale and wheat as well as grassland, amenity turf and managed turf.
Plant Growth Regulator
Abscisic acid
Gibberellic Acid
Thidiazuron
Trinexapac-ethyl
Triacontanol
Paclobutrazol

Plant Growth Regulator
Gibberellic Acid Plant Growth Regulator,Triacontanol Plant Growth Regulator,Paclobutrazol Plant Growth Regulator,Thidiazuron Plant Growth Regulator
shijiazhuang yihe-chem co.,ltd , https://www.yihe-chem.com
